Low Strain Integrity Testing (PIT)
Pile Integrity Testing and Assessment
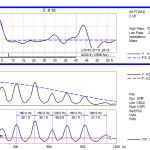
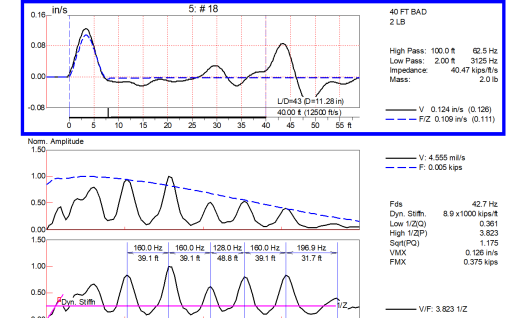
Low Strain Impact Integrity Testing is a non-destructive pile testing method for integrity assessments of augered cast-in-place piles, drilled shafts or driven concrete or timber piles. If major defects exist, test results may be interpreted to estimate their magnitude and location. Test results may also be used to estimate pile length.
The Low Strain Test, also known as Pile Integrity Test (PIT), encompasses the Pulse Echo Method and the Transient Response Method. Tests by either method are normally performed after foundation installation and curing, and require minimal pile preparation. Because of their simplicity, speed of execution and relatively low cost, these integrity tests may be performed on 100% of the piles on a given a job site. In some cases piles in existing foundations can be tested.
The GRL engineer hits the top of the foundation with a handheld hammer. The impact of the hammer generates a compressive stress wave in the pile or shaft, and an accelerometer placed on top monitors the motion associated with this wave. The stress wave propagates down the pile shaft and is reflected when it encounters either the toe or a non-uniformity of the shaft. These reflections cause a change in the acceleration signal measured on the pile top, which is picked up and processed by the Pile Integrity Tester (PIT) equipment and interpreted by an experienced GRL engineer.
Depending on job conditions and requirements, GRL performs the test by the Pulse Echo Method (using a non-instrumented handheld hammer) or by the Transient Response Method (an instrumented hammer is used).
Pile Integrity Testing has been routinely used worldwide for many years; it is standardized by ASTM D5882 – Standard Test Method for Low Strain Impact Integrity Testing of Deep Foundations.